Gas Turbines
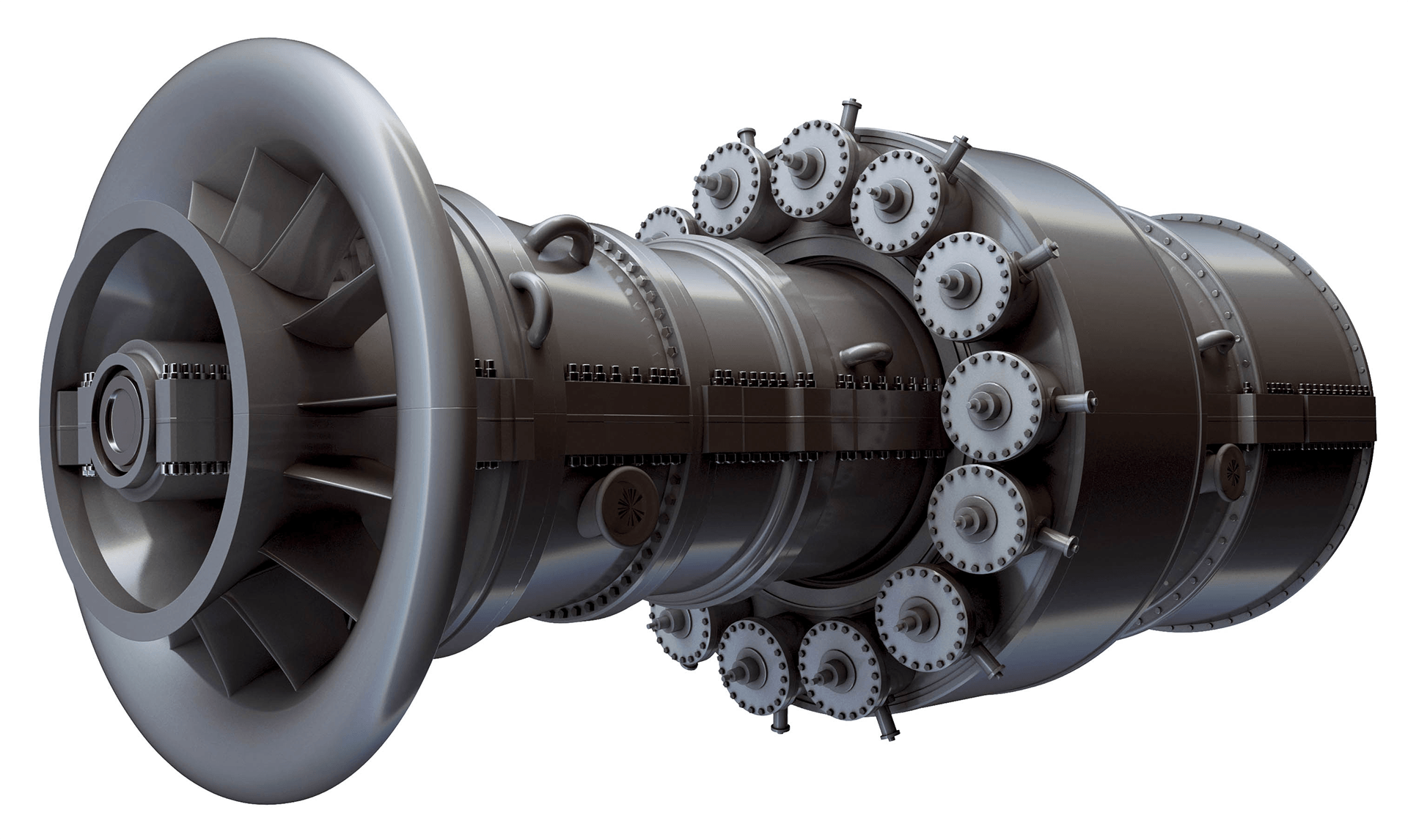
Advantages Of Gas Turbines
Compared to other power technologies, Solar gas turbines have a number of advantages
- Higher reliability and availability
- Lower operating costs
- Utilizes clean and other renewable fuels
- Lowers emissions
- High quality exhaust heat stream can be used in other processes
- High power density
- Broad range of power module blocks
- Reduces construction costs
- Easy to transport and quick startup
- Improve reliability
- Easy to permit
- Worldwide service and support
Gas Turbine Overview
A gas turbine engine is a type of internal combustion engine. Essentially, the engine can be viewed as an energy conversion device that converts energy stored in the fuel to useful mechanical energy in the form of rotational power. The term “gas” refers to the ambient air that is taken into the engine and used as the working medium in the energy conversion process.
This air is first drawn into the engine where it is compressed, mixed with fuel and ignited. The resulting hot gas expands at a high velocity through a series of airfoil-shaped blades transferring energy created from combustion to turn an output shaft. The residual thermal energy in the hot exhaust gas can be harnessed for a variety of industrial processes.
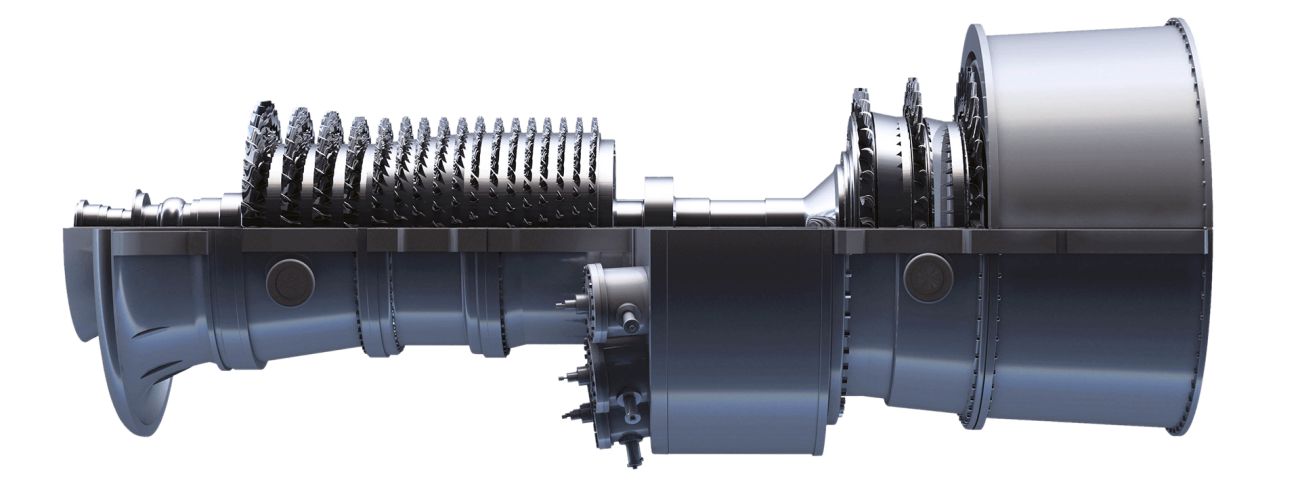
Basic Gas Turbine Components
Compressor – Takes in outside air and compresses it.
Combustor – Fuel is added to the pressurized air and is ignited.
Turbine – Converts the energy from high velocity gas into rotational power through expansion.
Output Shaft and Gearbox – Delivers rotational power to the driven equipment.
Exhaust – Directs the low emission spent gas out of the turbine section.
